Causes2
- Poor oral and facial muscle control
- Parkinson’s disease
- Cerebral palsy
- Intellectual disability
- Stroke

Symptoms2,8
- Excessive wetness
- Skin breakdown around the mouth
- Infection from skin breakdown
- Dehydration or not enough fluids
- Foul odor
External Effects3
- Greater risk of infection
- Skin irritation

Internal Effects3
- Risk of breathing problems or clogged airway
- Swallowing or feeding difficulties
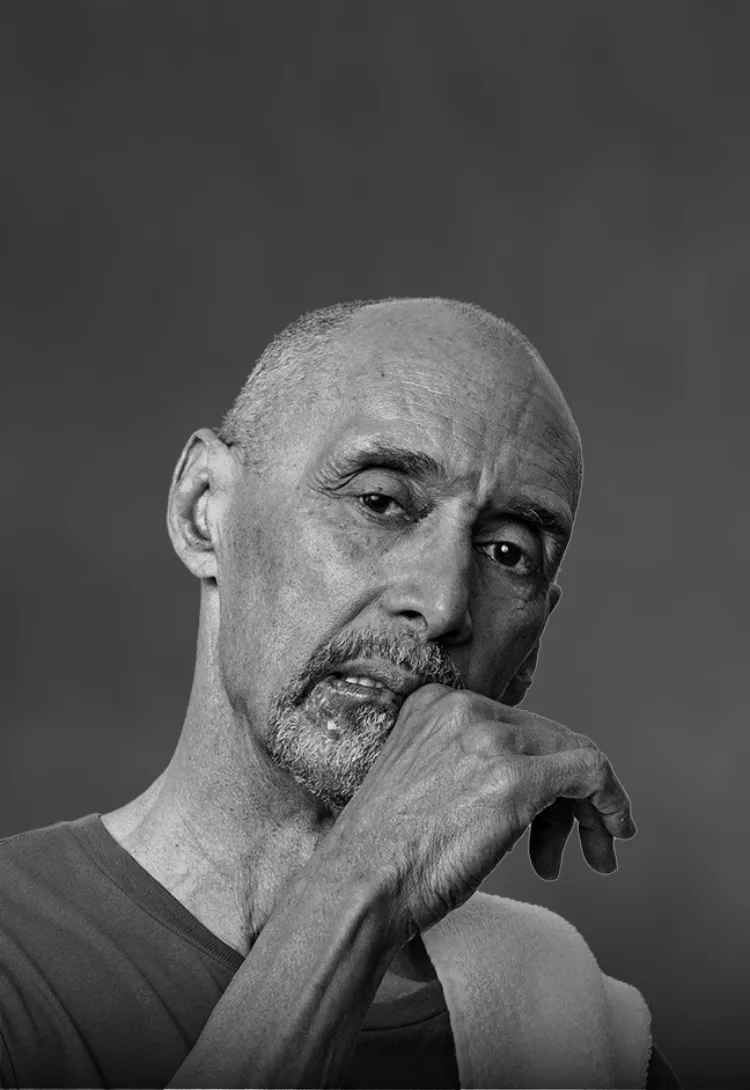
Luis is a 65-year-old Musician Who Always Marches to the Beat of His Own Drum
The life he's fighting for
Following his successful musical career, Luis now enjoys exploring the city’s food scene with friends and brushing up on his chess skills. When he’s not discovering the next best restaurant, Luis spends time with his 2 kids and 3 grandkids. Nothing comes close to the joy Luis feels when spending quality time with family and friends.
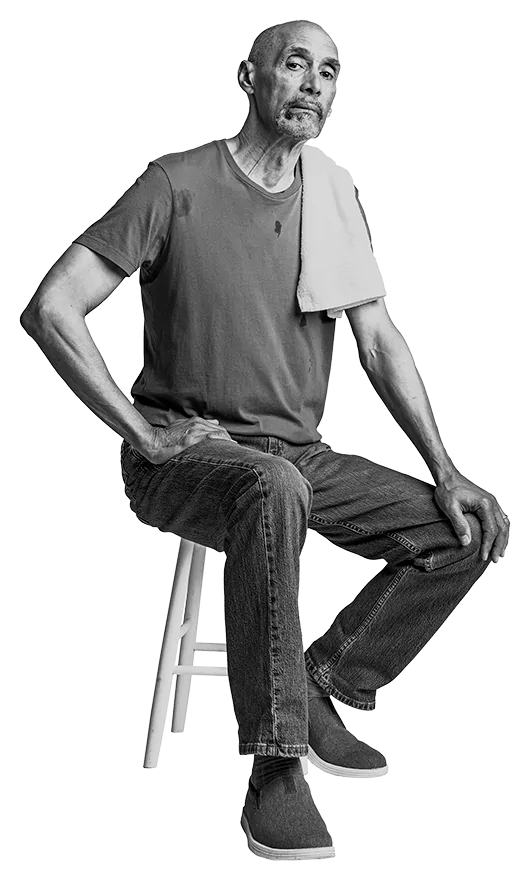

The weigh-in
- Luis developed chronic sialorrhea due to Parkinson’s disease (PD), which he has had for 6 years
- The excessive drooling can often be embarrassing and sometimes makes it harder to eat, enjoy a meal, and communicate with his loved ones
Sparring with chronic sialorrhea
- At first, Luis received no treatment and sialorrhea symptoms took charge of his life
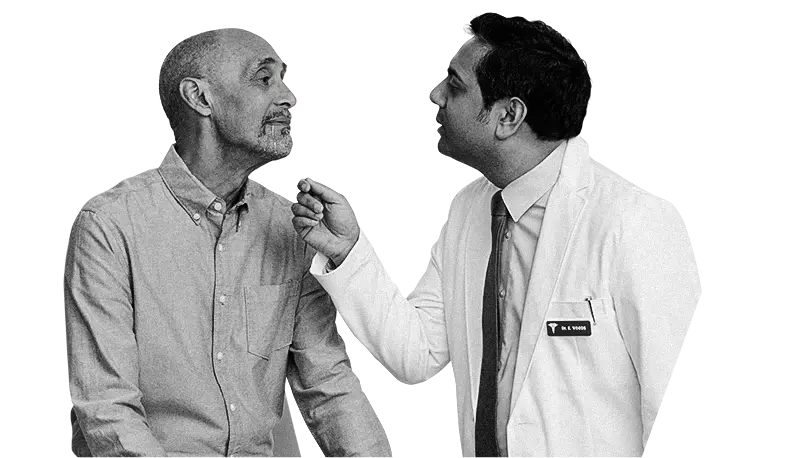
- Having to use a towel on his pillow at night while suffering from frequent coughing urged Luis to have a serious conversation with his doctor
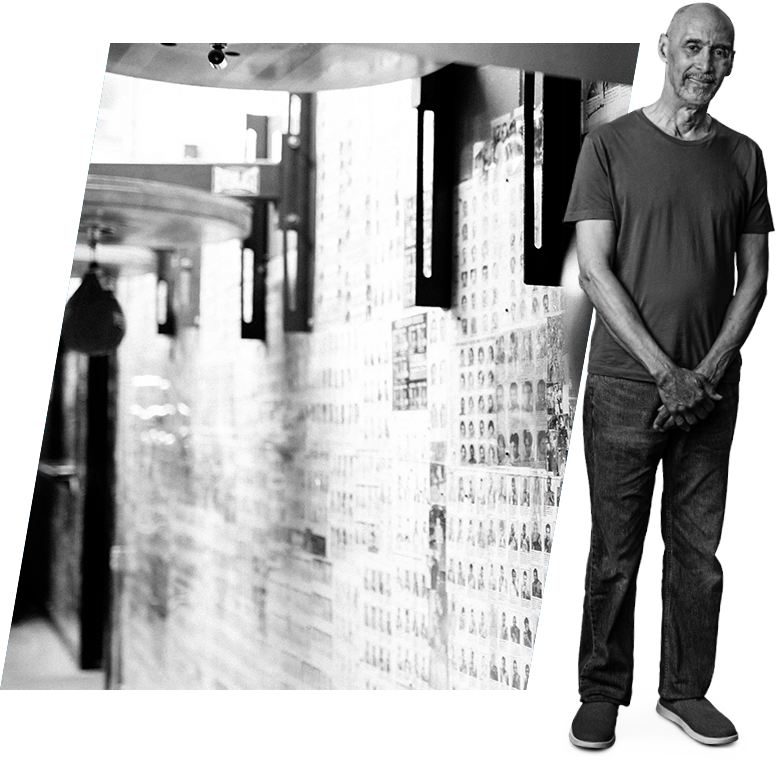

Never defeated, Luis adjusted his plan of attack
Explore XEOMIN for the treatment of adult chronic sialorrhea
See the XEOMIN Difference